First Aid Tips During an Asthma Attack
Asthma is a chronic respiratory health condition that affects millions globally. It’s marked by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to breathing difficulties. When symptoms intensify, an asthma attack occurs, which can be life-threatening if not handled promptly. Recognizing triggers, early signs, and knowing effective first aid tips can be critical in managing asthma effectively.
Common Triggers of an Asthma Attack
Asthma attacks often occur due to various triggers that cause airways to become inflamed and constricted. Key triggers include:
Allergens
Dust mites, pet dander, pollen, mold, and certain foods can trigger allergic reactions, setting off asthma symptoms.
Pollution and Smoke
Airborne pollutants, like vehicle exhaust, smoke from fires, and industrial emissions, irritate the lungs, often causing asthma attacks.
Cold Air
Breathing in cold air can constrict the airways, triggering asthma symptoms. This is common in colder climates or winter months.
Physical Activity
While exercise is beneficial, it can cause exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in some individuals. High-intensity activities like running or cycling may exacerbate symptoms.
Stress and Emotions
Strong emotions, whether stress, anger, or excitement, can affect breathing patterns and trigger an attack.
Respiratory Infections
Colds, flu, and other respiratory infections can inflame the airways, making individuals more susceptible to asthma attacks.
Identifying and managing these triggers is essential to prevent frequent asthma attacks. Many people find it helpful to keep an asthma diary to track triggers, symptoms, and response to medications.
Early Signs of an Asthma Attack
Recognizing early signs allows for prompt action, potentially preventing a severe attack. Common signs include:
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing is a hallmark symptom, especially during physical activity or when exposed to triggers.
- Wheezing: This high-pitched whistling sound during breathing indicates that the airways are partially blocked.
- Coughing: Frequent, persistent coughing, especially at night, is an early warning sign of an impending attack.
- Chest Tightness: Many experience a sensation of tightness or pressure in the chest, which can worsen as the attack progresses.
- Fatigue: Increased tiredness or exhaustion due to less oxygen intake can be an early sign of an asthma attack.
- Difficulty Sleeping: Asthma symptoms may intensify at night, disrupting sleep and leaving one feeling exhausted.
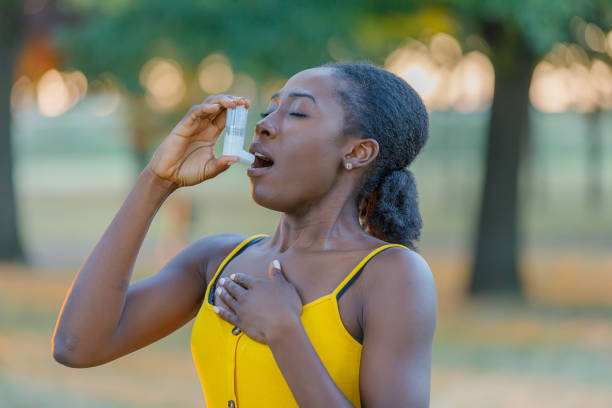
First Aid for Asthma Attacks
If someone is experiencing an asthma attack, quick and effective first aid can be crucial. Here are essential steps to follow:
- Stay Calm and Offer Reassurance: Anxiety and panic can worsen symptoms. Encourage calm, steady breathing to help keep airways as open as possible.
- Use an Inhaler with a Spacer: If the person has a rescue inhaler, help them use it immediately. Ideally, use a spacer for more effective delivery of medication.
- Dosage: Typically, one puff is administered every 30-60 seconds up to 10 puffs. If symptoms persist after 10 puffs, seek emergency assistance.
- Position for Comfort: Have the person sit upright, which helps open the airways. Avoid lying them down as it can make breathing more difficult.
- Remove Triggers: Move the person away from any known triggers, such as smoke or dust, to reduce irritation.
- Seek Medical Help if Necessary: If the attack does not subside or symptoms worsen, call emergency services. Severe symptoms, like extreme shortness of breath, blue lips or fingernails, or inability to speak, indicate a medical emergency.
Prevention and Long-Term Management of Asthma
Preventive steps can reduce the likelihood of asthma attacks and improve overall quality of life:
- Avoid Known Triggers: Identify and minimize exposure to personal triggers as much as possible. Air purifiers, avoiding smoking areas, and regular cleaning can help.
- Regular Medication: Many individuals benefit from daily asthma medications, such as corticosteroids, which help control inflammation. A healthcare provider can determine the right medications and dosages.
- Regular Monitoring: Using a peak flow meter at home can help track lung function and detect subtle changes, allowing early intervention before an attack.
- Asthma Action Plan: Work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized asthma action plan, outlining specific steps to take when symptoms worsen.
When to See a Doctor
Persistent asthma symptoms, frequent use of a rescue inhaler, or reduced daily activities due to asthma are signs to consult a doctor. Asthma severity can change over time, so regular check-ups and adjustments in the management plan may be necessary.
In Summary
Asthma is a manageable condition, and understanding triggers, recognizing early signs, and knowing how to administer first aid can make a significant difference. Regular monitoring, avoidance of triggers, and proper medication can prevent severe attacks and lead to a better quality of life. Remember, each person’s asthma is unique, so what works best will depend on individual circumstances and medical guidance.