
Demonstrate Osmosis
Here we Delve Into how to Demonstrate Osmosis in Living Tissues: A Practical Guide in Kenya 2025.
Osmosis is a critical process in biology, influencing how water moves in and out of cells. Understanding this concept is vital for students and professionals alike.
This article will define osmosis, explain the definition of osmosis in biology, and provide examples of osmosis. Additionally, we will offer a practical demonstration using locally available materials in Kenya 2025.
Defining Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from a region of lower solute concentration to a region of higher solute concentration.
This movement aims to equalize the solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane. The definition of osmosis is essential in understanding various biological processes.
Definition of Osmosis in Biology
In biological terms, osmosis is a type of passive transport, meaning it does not require cellular energy.
The definition of osmosis in biology refers to the movement of water across a cell membrane driven by a concentration gradient.
This osmosis process is crucial for maintaining cell turgor pressure, which supports the structural integrity of plant cells and is vital for the proper functioning of all living cells.
Examples of Osmosis in Biology
To grasp the concept better, let’s look at some practical examples of osmosis:
- Plant Roots Absorbing Water: Plants absorb water from the soil through osmosis. Water moves from the soil (low solute concentration) into the root cells (high solute concentration).
- Red Blood Cells in Different Solutions: Placing red blood cells in a hypertonic solution (high solute concentration) causes water to leave the cells, making them shrivel. Conversely, in a hypotonic solution (low solute concentration), water enters the cells, causing them to swell and potentially burst.
Demonstrating Osmosis in Living Tissues in Kenya 2024
To demonstrate osmosis using living tissues, we can conduct a simple experiment with locally available materials. This demonstration is not only effective but also relevant to the Kenyan context, on how to Demontrate Osmosis in Living Tissues.
Materials Needed:
- Sweet potato or Irish potato
- Knife
- Table salt
- Distilled water (available at local pharmacies)
- Two transparent containers
- Weighing scale (common in markets)
Procedure:
- Prepare the Potato Slices: Peel and cut the potato into two equal slices.
- Weigh the Potato Slices: Use the weighing scale to record the initial weight of each slice.
- Prepare the Solutions: Fill one container with distilled water and label it as the control. In the other container, create a salt solution by dissolving salt in distilled water.
- Immerse the Potato Slices: Place one potato slice in the container with distilled water and the other in the container with the salt solution.
- Wait for Osmosis to Occur: Allow the slices to sit for at least one hour.
- Weigh the Potato Slices Again: After the waiting period, remove the potato slices from the containers, gently pat them dry, and weigh them again.
Observations and Results:
- The potato slice in the distilled water will gain weight as water moves into the cells by osmosis.
- The potato slice in the salt solution will lose weight as water moves out of the cells to the surrounding solution.
Explanation of the Results
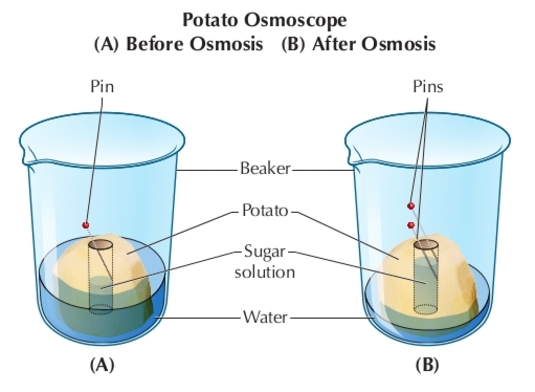
The potato in the distilled water (hypotonic solution) absorbs water, demonstrating osmosis in biology. This movement of water into the cells increases their turgor pressure, making the potato slice firm.
In contrast, the potato in the salt solution (hypertonic solution) loses water, illustrating the osmotic definition where water moves out of the cells, resulting in a loss of turgor pressure and a limp potato slice.
Thus, we’ve successfully manage to Demontrate Osmosis in Living Tissues.
Conclusion
Understanding the definition of osmosis, the definition of osmosis in biology, and seeing an example of osmosis through this simple potato experiment provides a clear demonstration of how osmosis works in living tissues.
In Kenya, using locally available materials makes this experiment accessible and practical for students and educators. Osmosis is a fundamental process that is crucial for maintaining the balance of fluids in biological systems and is integral to the health and function of cells.
This experiment is a straightforward and effective way to observe osmosis in action and to grasp its significance in biology.
By demonstrating osmosis with easily accessible materials, we can make complex biological concepts understandable and relevant, fostering a deeper appreciation for science in everyday life.







